Explainable and interpretable bearing fault classification and diagnosis under limited data
Abstract
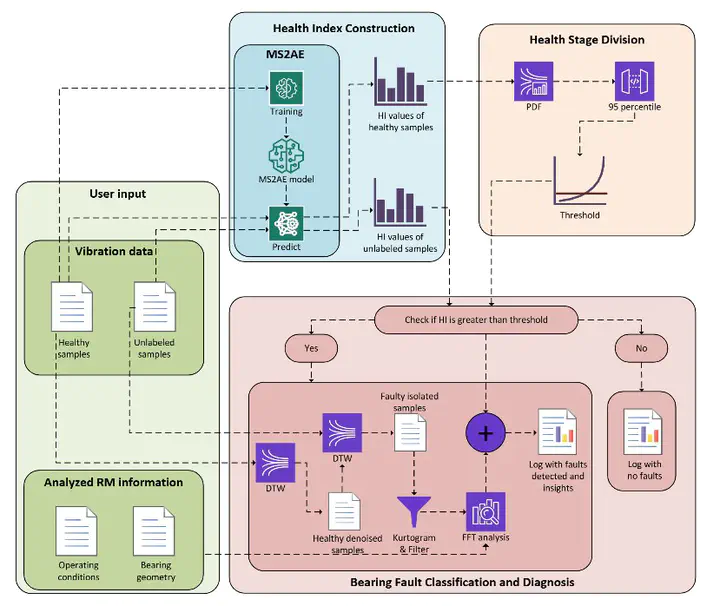
Rotating machinery plays an essential role in various industrial processes such as manufacturing, power generation, and transportation. These machines, which include turbines, pumps, motors, compressors, and many others, are the heartbeats of numerous industries. The seamless operation of these machines is critical for the efficiency and productivity of these sectors. However, over time, these machines degrade and can suffer faults. One of the most critical components are bearings, which can suffer different types of faults. This paper presents a novel approach for bearing fault classification and diagnosis under limited data. A Monotonic Smoothed Stacked AutoEncoder (MS2AE) is used to infer a smoothed monotonic health index from raw bearing acceleration data. The MS2AE is trained using only healthy data, so this approach can also be used with recently comisioned equipment that has not failed yet. The explainability provided in the health index construction process makes the system useful in certain industries where black-box AI models cannot be trusted due to strict regulations. The classification and diagnosis system achieves robustness in fault classification under different working conditions by utilizing multiple bearing fault datsets. Its ability to be trained using only healthy data and the interpretability offered, makes it suitable for recently installed rotating machinery in real industrial facilities, without requiring qualified staff.