Abstract
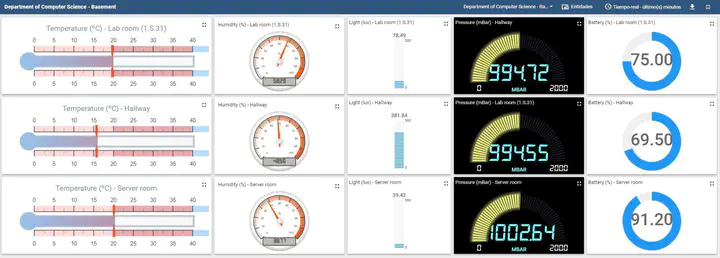
Wireless sensor networks are usually deployed in mesh topologies using radio communication links. The mesh selforganizes to route data packets from sensors to the sink. However, if not carefully designed, this may create holes of uncovered areas and energy holes when many networks paths traverse a limited number of sensors. This paper presents the design and performance evaluation of a low-cost clustered wireless sensor network for Building Energy Management (BEM) applications using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and Better Approach to Mobile Ad-hoc Networking (BATMAN). The latter is used to interconnect gateways and cluster headers that have enough power to forward packets and make computations without compromising their battery lifetime, while the former is used to connect sensors to a cluster header. A prototype of a BEM application has been developed and the performance of the network was tested. Results show that the throughput and latency achieved are adequate for BEM applications.